Honey is a natural sweetener that has been used for thousands of years for its medicinal properties. Honey contains several active compounds that have been shown to help with disease and has been traditionally used in the treatment of eye diseases, bronchial asthma, throat infections, tuberculosis, thirst, hiccups, fatigue, dizziness, hepatitis, constipation, worm infestation, piles, eczema, healing of ulcers, and wounds and used as a nutritious supplement.
Medicinal Uses of Honey
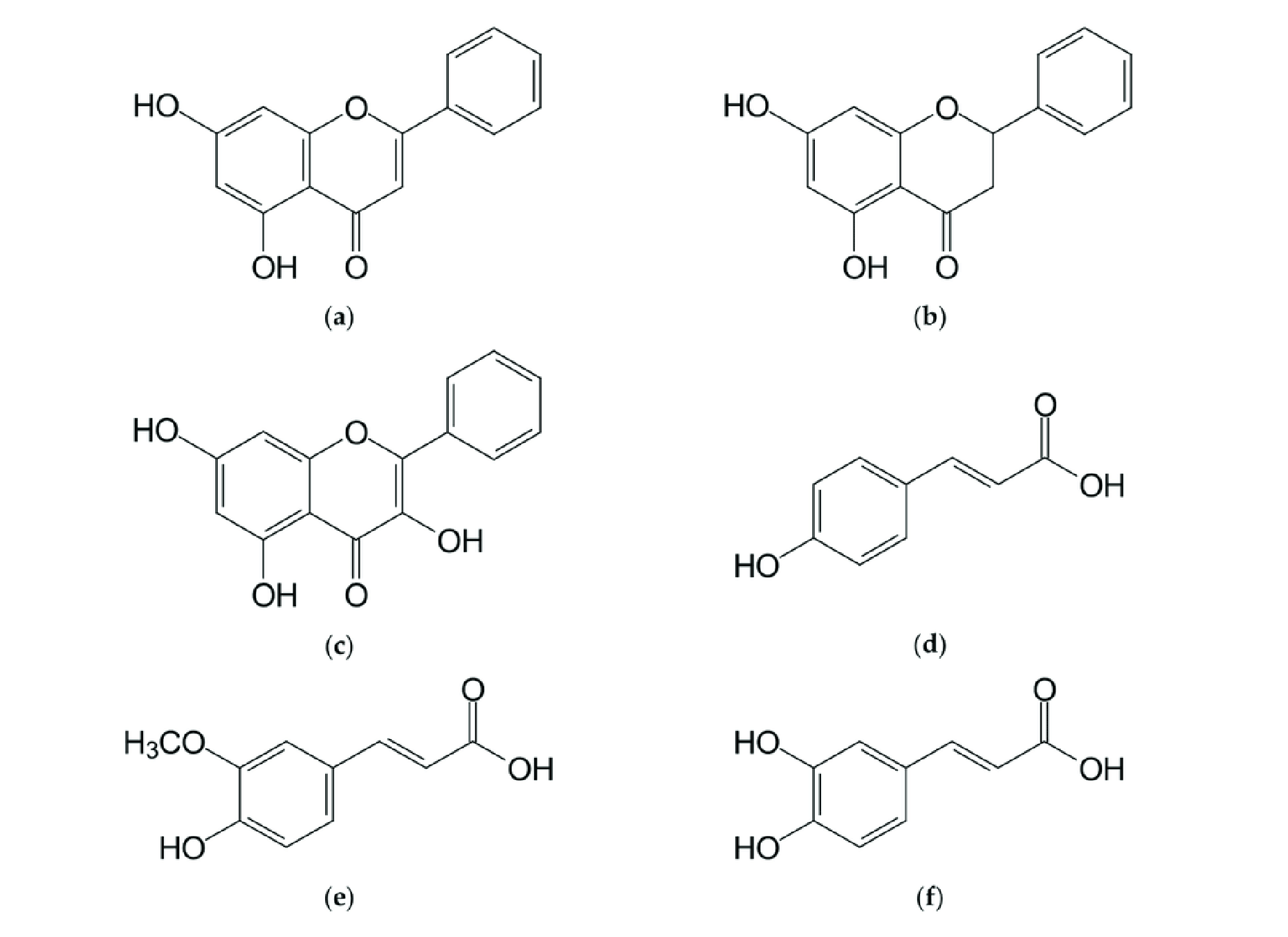
Honey's content in flavonoids and phenolic acids plays a key role on human health, thanks to the high antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that they exert. Honey possesses antimicrobial capacity and anticancer activity against different types of tumors, acting on different molecular pathways that are involved on cellular proliferation.
In addition, an antidiabetic activity has also been highlighted, with the reduction of glucose, fructosamine, and glycosylated hemoglobin serum concentration. Honey exerts also a protective effect in the cardiovascular system, where it mainly prevents the oxidation of low-density lipoproteins, in the nervous system, in the respiratory system against asthma and bacterial infections, and in the gastrointestinal system.
Raw honey's compounds have also been helpful fighting cancer because it contains several active compounds:
- Methylglyoxal (MG): MG is a natural compound that has been shown to kill cancer cells in vitro and in animal studies.
- Polyphenols: Honey is a rich source of polyphenols, which are plant compounds that have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Flavonoids: Flavonoids are another type of polyphenol that has been shown to have anti-cancer properties.
- Other compounds: Honey also contains other compounds with potential anti-cancer properties, such as propolis, royal jelly, and bee pollen.
Honey Benefits
Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Honey contains antioxidants, which can protect the body from inflammation. Inflammation can lead to a variety of health issues, including heart disease, cancer, and autoimmune disorders.
Cough and Sour Throat Relief for Children
Health authorities do not recommend over-the-counter medications to treat young children's coughs and colds. Parents can look for natural remedies such as using teaspoons of the best raw honey relieved children's nighttime cough and allowed them to sleep.
Minerals and Compounds
Honey has about 31 different minerals like phosphorus, magnesium, and potassium. It also has several important amino acids (the building blocks of protein).
Antioxidants
Honey is high in polyphenols and flavonoids, which act as antioxidants. That means they help protect your body against some types of cell damage.
Wound and Burn Healing
For many years, honey has been used to treat burns and wounds. Its antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties may ease burns and improve wound healing and the honey keeps the skin moist so that it can heal. When raw honey is infused with lavender, the wound and burn healing is further soothed.
Cholesterol
Research has also found that raw honey may help reduce cholesterol. Levels of total cholesterol, LDL (or "bad") cholesterol, and triglycerides tend to go down with people who had 70 grams of honey (about 2.5 ounces) each day for 4 weeks. Their HDL (or "good") cholesterol also increased.
Honey Risks
Is honey safe for everyone? Honey is a safe food for most people, but not for all. Here are some potential risks of eating honey, including raw honey:
Botulism in Infants
You should not give honey to infants under 12 months. Honey contains dust particles that may carry spores of the bacteria, Clostridium botulinum, that causes botulism. Because a baby's immune system is still developing, these spores can cause infant botulism, which could cause them to get very sick. Using honey in cooking food for children should be safe, as heat destroys most bacteria.
Infant botulism is a rare but serious illness that attacks your child's nerves. The first sign is usually constipation. Your baby may also have muscle weakness, which means they might have trouble feeding and breathing, and a weak cry.
Allergies
People who are prone to allergies should be careful about eating honey. Although honey allergies are rare, they do occur. This is because of the bee pollen in the honey. Bee pollen is a mixture of pollen and digestive enzymes from bees. It can trigger a serious allergic reaction. You're more likely to find pollen in raw honey.
Some people say that eating local honey improves their seasonal allergies. They believe the pollen in the honey desensitizes them to pollen in the air. There is not enough evidence to support this. It could be harmful to rely on honey rather than seeking medical treatment for respiratory allergies.
Symptoms and signs of an allergic reaction include:
- Wheezing
- Fainting
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Irregular heart rhythm
- Excessive sweating
- Weakness
Honey and Your Microbiome
Many of you might be familiar with the idea that your diet affects your gut microbiome, which in turn affects your overall health. But just going outside and interacting with nature is one of the most powerful things you can do to influence the health of your gut microbiome
The natural environment offers an abundance and diversity of beneficial microbes. Interacting with nature provides the opportunity for beneficial microbes to establish in your gut, support your immune system, and help you become more resilient to inflammation and disease.
There is a growing body of research showing that the environment around you influences the collection of microbes that inhabit different parts of your body, including your digestive system. The environment may even contribute more to your microbiome than genetics. Scientists are studying the loss of biodiversity (variety of life) in our natural environment as one reason for the increases in inflammatory diseases.
- Studies comparing populations from around the world have found higher gut bacterial species richness among people living in rural environments compared to those living in urban areas, possibly because rural environments offer the opportunity to be exposed to greater biodiversity of living organisms compared to urban environments.
- Having more plant species growing in the landscape around your home is found to having greater diversity of bacteria on the skin and can prevent atopic allergies.
- Adding sod and vegetation can increase the richness and diversity of beneficial bacteria and lowers pathogenic bacteria.
- Just rubbing your hands with soil and plant material increases beneficial microbial diversity in the gut and skin.
Getting Closer to Nature When You Can't Get Outside
The National Library of Medicine has researched the benefits of raw honey on the gut. In their research, they review the current and growing evidence that shows the prebiotic potential of honey to promote healthy gut function, regulate the microbial communities in the gut, and reduce infection and inflammation. Because raw honey contains prebiotics, honey can be used to promote specific, favorable changes in the composition and function of the gut microbiota.- Honey contains non-digestible carbohydrates in the form of oligosaccharides, and there is increasing evidence from in vitro, animal, and pilot human studies that some kinds of honey have prebiotic activity.
- The gut microbiota combats gut inflammation and the development and progression of numerous conditions, such as colon cancer, irritable bowel syndrome, obesity, and mental health issues.
- Raw honey can reduce the presence of infection-causing bacteria in the gut including Salmonella, Escherichia coli, and Clostridiodes difficile, while simultaneously stimulating the growth of potentially beneficial species, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacteria.
No matter the season, there is opportunity to expose ourselves to nature and raw honey. You can catch all the beneficial microbes you can from nature whether its gardening in the soil, swimming in the ocean, or consuming the best raw honey. If you live in an unpolluted environment, just being outside, breathing fresh air, and exposing your body to the outdoors can benefit your gut microbiome. If you live in an urban environment, consider spending more time in the parks, or taking a trip to hike in a forest. Nature and honeybees are your friend--embrace it!


















Leave a comment